ASPION customer portal - Worth knowing
With our whitepapers and other material on various topics related to transport, we want to provide you with valuable background information. Here you can find out, for example, which accelerations occur or which loads goods can be exposed to in intermodal transport. In addition, a video shows a shaker that performs an acceleration of 6 g. We wish you informative reading! If you have any questions, please do not hesitate to contact us via our support or the contact form.
Transport regulations regarding batteries and transmitter functions
Lithium batteries are classified as dangerous goods in international transport rights. This means that they are subject to a wide range of regulations for the transport of dangerous goods. ASPION G-Log data loggers also use lithium metal button cells. In the case of air freight transport, additional transmission functions are also important.
The good news first: Due to ADR 2021 section 5.5.4.1, ASPION G-Log data loggers are exempt from the obligation to label batteries. Bluetooth operation in accordance with IATA DGR is also permitted for air freight transport.
The document ASPION Data Loggers and Transport Regulations explains the background and regulations in detail, links to important information and gives useful practical advice. Please note that the document illuminates the view on regulations as a company based in Europe and may differ in other countries.
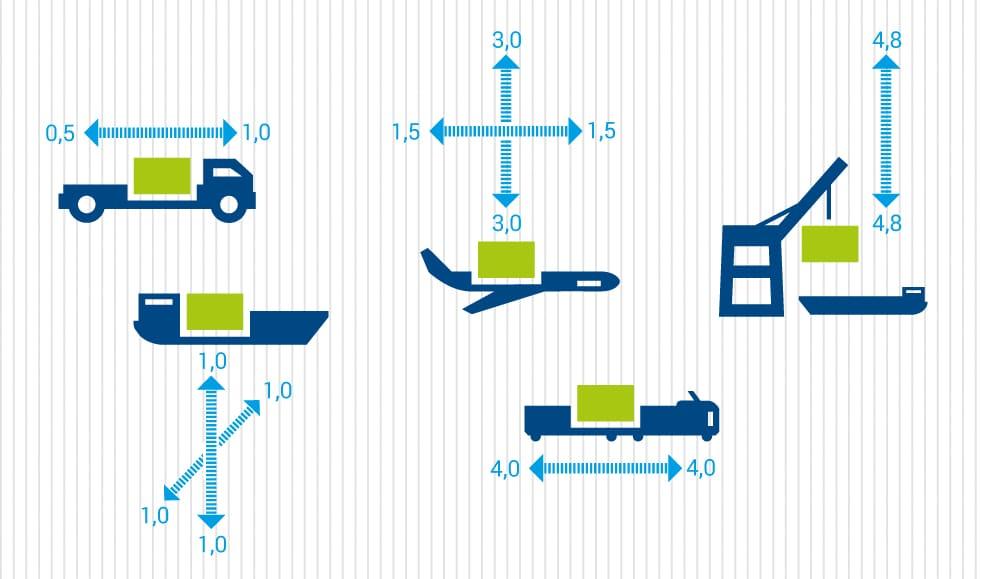
Loads during the global transport of goods
In globalised goods traffic, around one in three deliveries is rejected due to transport damage. You can read about the stresses that export goods are exposed to per se when transported by truck, ship or air freight, the accelerations that occur, for example, when handling containers, and how to find the right settings for the use of digital data loggers in our white paper - with the kind support of GDV, Gesamtverband der Deutschen Versicherungswirtschaft e.V. (German Insurance Association).
Effect of accelerations
The whitepaper gives you some hints on the effect of accelerations with some examples.
What does an acceleration of 6 g look like?
The following film shows a comparison measurement of ASPION G-Log shock sensors, which was carried out at the Fraunhofer Institute ICT with a so-called shaker. Six ASPION G-Log shock sensors were mounted on the shaker and subjected to an acceleration of ± 6 g. The shaker was used for the measurement of the G-Log shock sensor. The values recorded by the sensors deviate on average by only 2.5 % from the acceleration values recorded by the shaker. A measurement directly on the acceleration sensor shows that the housing does not attenuate the shock value.


